Quick Overview:
When developing software, selecting a reliable software process model is a vital task. Software development models are the primary pillars for ensuring the application’s quality, performance, and stability. It helps the project teams determine the core processes and efficiently support completing them.
If you are currently working or want to make your career in the development domain, you must have a clear insight into software engineering models and methods.
Let’s get started and learn about types of SDLC and their processes.
Why do we need a Software Process Model?
If you don’t use an SDLC model, there can be a probability of missing something. So, let’s understand what is software engineering models, their methods, needs, and how they help us.
- We learn about the crucial steps for building a secure, scalable, and robust application aligned with industry standards.
- It helps assess the project cost and time and minimize the business and technical risks in the future.
- Leads to cover the edge-to-edge requirements and assures of constructing a top-notch application.
- It improves the collaboration between the project team and all the stakeholders.
- It makes the designing, development, testing, and maintenance operations seamless, stable, and smooth.
- Both client and project team understand the scope of creating the application accurately.
Understanding the Basics of Software Development Models
We know the benefits and needs of aligning projects according to software engineering models and methods.
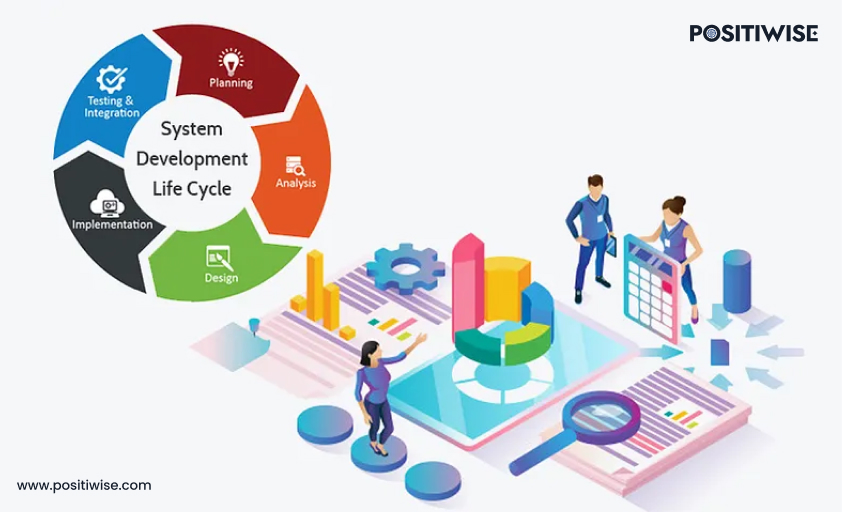
Various types of SDLC models are available, which you can select at your convenience. Still, before that, you should know the basic steps every model includes, and you should consider them for every project.
Step 1: Requirement Gathering and Analysis
The first step associated with any software delivery model is to collect the business requirements, focusing on the essential and most fundamental information.
Every detail you gather at this stage is essential, as it helps to make relevant decisions about the project, such as complexity, technology to be used, time-to-market, and so forth. In addition, you can precisely understand the risks affecting the quality of the software.
By focusing on requirement collecting, you can plan the development precisely and effectively, minimizing risk and assuring a cutting-edge solution.
Step 2: Generating Scope, Business, and Technical Goals
After collecting and assessing all the data, you have to create a project scope, which should define what will be your final product or output at the end of this software development model.
In this stage, you will describe the functionalities of your application, including both backend and frontend. As a result, an SRS, formerly a Software Requirement Specification document, will be created and shared with the client for approval.
The client will verify the application details by reviewing the SRS, and the development team will use it for internal purposes.
Step 3: Scheduling and Planning
When the client finals all its requirements, you have to create a project plan for an efficient roadmap to complete the project before the deadline.
You have to perform all the resource, cost, and time-related analyses at this step only; otherwise, your project can face non-preventive risks in the future. Once you are done with all the planning and ready with your project charter and other crucial plans, you can initiate the designing phase.
Step 4: Designing
In this stage of SDLC, multiple software designs are drafted, including the interface and architectural designs. In addition, the development team creates a Design Document Specification for further help.
This vital document lists all the details about fabricating modules and overall architecture. Once the designing team specifies all the aspects by curating wireframes, prototypes, and mockups, you can move your project to the development phase.
Step 5: Development and Testing
It is the building stage of your software and one of the key processes. The software development team utilizes all the applicable documents, wireframes, and technologies for innovating a top-notch business application, which must align with the organization’s guidelines.
Interestingly, DDS plays a significant role in this step. Detailed design documentation can aid the software developers and architects in smoothly executing the operations and rapidly concluding a best-in-class software.
Once the software engineers create the application, testers come into the role and check the functionality and security to ensure there are no vulnerable loopholes, glitches, and errors. After thoroughly testing the app, the client gets its application delivery.
Step 6: Maintenance and Support
Monitoring, testing, fixing, and maintaining the software are post-development operations that are highly necessary for every project.
The primary objective of this phase is to undergo application through user acceptance testing and verify whether all the functions are properly working or not. Moreover, the company assesses whether the users are ready to adopt the software or not.
As a result, the project team tries to eliminate the drawbacks and correct the software for the final release. When the software is finally active and live, the support team continuously monitors it and ensures its seamless functioning and quality of service.
Types of SDLC: Software Development Models with Examples
Waterfall Model SDLC
The Waterfall Model SDLC is the most basic and earliest software development model, invented and introduced to the public between the 1950s and 1970s.
It is a straightforward approach, comprising only the fundamental steps associated with any SDLC, namely:
- Requirement Gathering and Planning
- Designing
- Development
- Testing
- Software deployment
- Maintenance and Support
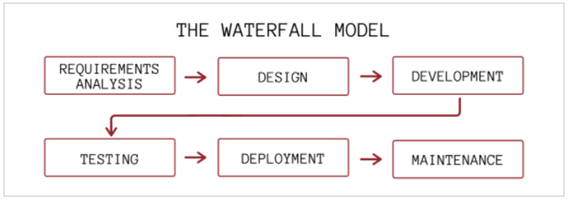
From the name Waterfall, you can easily understand that it is sequentially linear, meaning you can’t escalate the project to the next step until the current phase is in an active state.
For example, if you collect information from the stakeholders in the first step, you cannot initiate the designing phase until you have documents containing all the details. In simple terms, the output of one phase functions as an input for the upcoming one.
V-Model
V model is an advanced version of the Waterfall software development model with testing associated with every phase.
Its name, V-model SDLC, is derivated from the Validation and Verification processes. These are also the two primary objectives of using this approach. Every testing included in this model verifies the software as per the requirements validated by the clients.
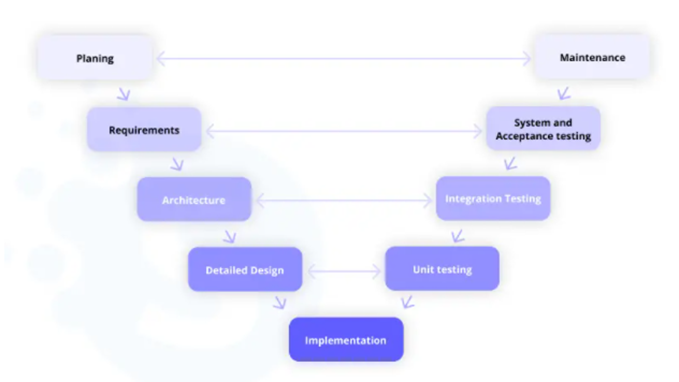
As we have seen in the waterfall model, you can’t move further without completing the current phase, and the same is the case with the V-model.
For example, you can only move ahead from the architecture development phase when the integration testing results verify the project scope and goals.
Spiral Software Model
Spiral is one of the most flexible SDLC models, and experts are highly considering it for developing large-scale and complex applications through its modular approach.
The waterfall and prototype model features to assure the seamless execution of the overall procedure and guarantee the desired application as the final result.
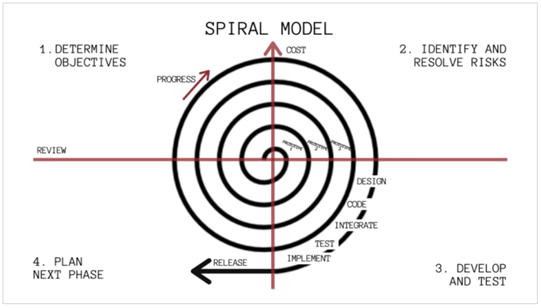
A significant benefit of this model is its risk identification and resolution phase, which helps discover potential threats that can affect the cost, time, quality, and other project resources and KPIs. Once you align your application development with the spiral model, it will continually revolve around its four significant stages for resolving all the risks.
For example: If you are at the beginning of your project and following the spiral model. Then, you will first define the objective and analyze it to find and resolve risks. Further, start with design, development, and testing.
And, if you discover any new thing, you will shift your project to the 4th stage, known as planning the next phase. Only the spiral will end when you and your client are satisfied with the application.
Agile Model
You must have heard about this SDLC mechanism very often. IT firms prefer Agile for software projects, but other industries adapt their methodologies to provide quality work to their clients.
The fundamental steps in software engineering best practices models allow for the creation of multiple iterations, leading to the development of software that fulfills all requirements. Each iteration in this process requires effective engagement and collaboration between the team and stakeholders.
For Example: Once you are at the development stage and the user interface is ready. You share the interface with stakeholders, and some changes are there. It will lead you to initiate that UI development iteration again.
That’s how iterations work in the Agile SDLC model.
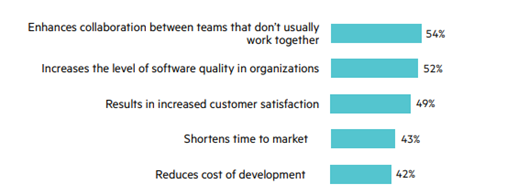
In addition, as per the industry data, Agile reduces development costs up to 42%, increases customer satisfaction by 49%, shortens time-to-market by 43%, and enhances software quality by 52%.
| Pros | Cons | Relevant for Project Having |
|---|---|---|
| Saving time and resources due to less documentation | Only experienced people can work on such projects, increasing the budget. | Probability of new changes every week |
| Saving of time and resources due to less documentation | High risk of failure, if stakeholder requirements are constantly changing | Briskly moving market |
| All the stakeholders actively participate | New development niche | |
| Issues are impeccably identified and mitigated | ||
| High-quality software is assured |
DevOps Model
DevOps Model SDLC is the new and latest entry in software development models. The application development and operations teams collaborate with this model to reduce the timeline and innovate a robust application.
The primary aim of this model is to make the overall process consistent and reduce the risks post-delivery of the solution.
With the growing industry needs and urgent need for business-oriented applications, the demand for DevOps experts is immensely breaking the bracket. And it is expected that 2026 it will be the most appraised SDLC model.
Incremental Model
The fundamental idea of developing this model comes from modernizing the waterfall approach by linking it with an iterative process, the incremental model SDLC modern software development is usually incremental and iterative.
This software process model comprises multiple mini waterfalls to fabricate the business solution and meet all client demands.
For example, suppose you are furnishing a large and complex application. In that case, developers will split the overall procedure into small iterations, and in each iterative circle, they will follow the waterfall model.
Every time you start an iteration, you have to follow all the stages included in the waterfall model.
Accelerate Your Business with Custom Software Solutions
Struggling with outdated or ineffective software? Our expert team provides custom systems designed specifically for your business needs. We analyze your operations, build solutions to fit your workflow and integrate with existing infrastructure.
Summing Up
Numerous SDLC models are available in the market, and you can choose any from them according to your project size and business requirements. The different model of software development has its guidelines, pros, cons, and suitability for different software projects.
Once you understand the fundamentals of the software development life cycle, you can quickly implement any model and ensure the success of your business software. In addition, as per the evolving industry, you must go for picking out Agile and DevOps methodologies, as these two are the most flexible and expert-preferred models.
Expert in Marketing Strategy and Brand Recognition
Jemin Desai is Chief Marketing Officer at Positiwise Software Pvt Ltd, he is responsible for creating and accelerating the company’s marketing strategy and brand recognition across the globe. He has more than 20 years of experience in senior marketing roles at the Inc. 5000 Fastest-Growing Private Companies.